Harnessing Microsoft Sustainability Manager for Australian Reporting Obligations

In the rapidly evolving landscape of sustainability, businesses worldwide are grappling with the need to not only adopt sustainable practices but also to meet stringent reporting obligations. Australia, in particular, has seen a significant shift towards enforcing sustainability regulations, requiring organisations to transparently report their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics. This shift has placed immense pressure on companies to ensure their sustainability data is accurate, comprehensive, and aligned with the new standards. Enter Microsoft Sustainability Manager—a cutting-edge tool designed to empower organisations to navigate these challenges with ease.
Understanding the Reporting Obligations in Australia
Australia is taking significant steps towards integrating sustainability into its corporate governance framework by moving towards mandatory climate-related financial disclosures. The government is set to require companies to be transparent about their environmental impact and the risks associated with climate change. This shift is aimed at ensuring that businesses provide clear, comparable, and reliable data on their sustainability efforts, aligning with international standards like those set by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
Under these new regulations, Australian companies will need to disclose detailed and accurate information on various environmental metrics, such as greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, climate-related risks, and strategies for managing these risks. Additionally, businesses must demonstrate how climate change might affect their financial performance and long-term viability, ensuring that stakeholders can assess the sustainability of their operations effectively.
These upcoming requirements represent a significant challenge for organisations, especially those that have not yet fully integrated sustainability into their data management and reporting processes. The need for comprehensive and consistent sustainability data is paramount, as companies must align their reporting with the new disclosure standards. Failure to meet these obligations could lead to regulatory penalties, damage to reputation, and a loss of investor trust.
The obligation to report will be phased in over several years, beginning with the largest and most economically significant organisations. Initially, publicly listed companies and large financial institutions will be required to comply, given their substantial impact on and exposure to climate-related risks. These entities will need to start reporting in 2025, providing detailed insights into their environmental impact and sustainability strategies. Over time, the reporting requirements will extend to encompass medium-sized enterprises and eventually smaller businesses, ensuring a comprehensive and consistent approach to sustainability reporting across all sectors of the Australian economy. This gradual implementation allows organisations adequate time to develop and enhance their data collection and reporting capabilities to meet the stringent new standards effectively.
In this context, it is crucial for businesses in Australia to prioritize the development of robust data management systems that can meet the stringent demands of the forthcoming mandatory disclosures. This will not only help them stay compliant but also enhance their credibility and competitiveness in a market increasingly focused on sustainability.
The Role of Data in Sustainability Reporting
Data is the foundation of effective sustainability reporting, serving as the critical link between a company’s sustainability initiatives and its ability to demonstrate compliance with regulatory obligations. In the context of Australia’s evolving sustainability landscape, the importance of precise, timely, and well-integrated data cannot be overstated. Companies are increasingly required to track and report on a broad spectrum of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, ranging from greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and energy consumption to water usage, waste management, and social impact initiatives. The quality of this data directly influences the credibility and accuracy of the reports that organisations produce, making it essential for meeting both regulatory and stakeholder expectations.
Data’s role in sustainability reporting begins with its collection. Companies must gather data from various sources, often spanning different departments, geographic locations, and even third-party suppliers. This data can include everything from utility bills and raw material usage to employee commute patterns and product life cycle assessments. The challenge lies not only in collecting this vast array of data but in ensuring it is accurate, consistent, and complete.
Once collected, the next step is data management and integration. For sustainability reporting to be effective, organisations need to consolidate data from disparate sources into a unified platform. This centralisation allows for better analysis and ensures that all data points are accounted for when compiling reports. However, this process is often complicated by the use of different data formats, varying levels of data quality, and the need for real-time updates. Advanced data platforms play a crucial role in overcoming these challenges by offering tools that automate data integration, validation, and cleansing processes.
Beyond integration, data analytics and interpretation are critical for deriving meaningful insights from sustainability data. Raw data, without context or analysis, offers little value. By leveraging advanced analytics and AI-driven insights, organisations can transform raw data into actionable information that can inform decision-making, identify areas for improvement, and forecast future trends. For example, predictive analytics can help companies anticipate the impact of regulatory changes or shifting market conditions on their sustainability performance. These insights not only enhance the quality of sustainability reporting but also enable organisations to be proactive in their sustainability efforts, aligning their strategies with long-term goals and regulatory expectations.
Another key aspect of data in sustainability reporting is transparency and traceability. Stakeholders, including regulators, investors, customers, and the public, increasingly demand that companies provide clear, transparent reports that can be traced back to their original data sources. This transparency is essential for building trust and credibility, particularly as greenwashing concerns become more prevalent. Accurate and well-documented data allows organisations to substantiate their sustainability claims, ensuring that reports are not only compliant but also trustworthy.
Finally, data’s role extends to the ongoing monitoring and improvement of sustainability practices. Sustainability reporting is not a one-time exercise but a continuous process of tracking, reporting, and refining. Real-time data monitoring enables companies to track their performance against sustainability targets, identify deviations or areas of concern, and implement corrective actions promptly. This continuous feedback loop is essential for driving long-term sustainability improvements and ensuring that organisations remain aligned with their environmental and social responsibilities.
What is Microsoft Sustainability Manager?
Microsoft Sustainability Manager is a comprehensive solution designed to empower organisations in their sustainability journey by streamlining the process of data collection, management, analysis, and reporting. As part of the broader Microsoft Cloud for Sustainability offering, this platform integrates cutting-edge technology with advanced sustainability frameworks, enabling companies to effectively monitor and improve their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
At its core, Microsoft Sustainability Manager is a unified data platform that centralises sustainability data from across an organisation, breaking down silos and providing a holistic view of sustainability metrics. This centralisation is crucial for businesses aiming to comply with increasingly stringent regulatory requirements, such as those being implemented in Australia. By bringing all relevant data into a single platform, organisations can ensure that their sustainability reports are accurate, consistent, and comprehensive, reflecting the true state of their ESG efforts.
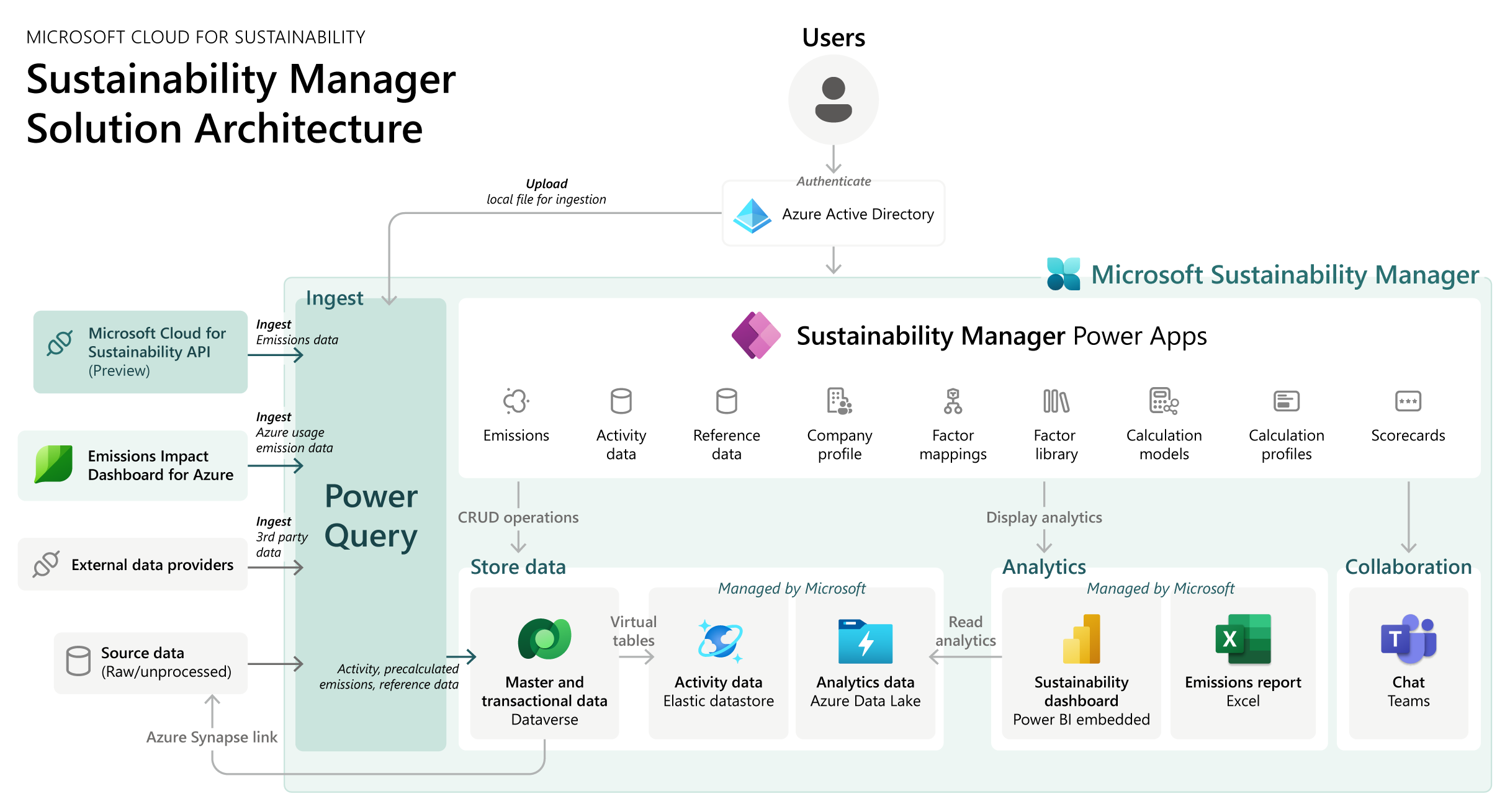
One of the standout features of Microsoft Sustainability Manager is its ability to automate and streamline the entire reporting process. Traditional sustainability reporting can be labor-intensive, requiring manual data collection, validation, and compilation across various departments and regions. Microsoft Sustainability Manager automates many of these processes, reducing the time and effort required to generate reports while also minimizing the risk of human error. This automation not only enhances the accuracy of sustainability reports but also allows organisations to produce them more frequently, providing up-to-date insights into their sustainability performance.
The platform also comes equipped with advanced analytics and AI-driven insights, which enable organisations to move beyond basic data reporting to derive deeper insights into their sustainability practices. By leveraging these tools, companies can identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that align with their long-term sustainability goals. For instance, predictive analytics can help forecast future energy consumption or GHG emissions, enabling organisations to take proactive steps to reduce their environmental impact.
Moreover, Microsoft Sustainability Manager is designed with flexibility in mind, offering customizable dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs) that cater to the unique needs of each organisation. Whether a company is focused on reducing its carbon footprint, improving water efficiency, or enhancing social governance practices, the platform can be tailored to track and report on the metrics that matter most to them. This level of customization ensures that organisations can align their reporting with both regulatory requirements and internal sustainability objectives, providing a clear and accurate picture of their progress.
Another critical aspect of Microsoft Sustainability Manager is its alignment with global and regional sustainability standards. The platform is designed to support compliance with a wide range of frameworks, including the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and the upcoming regulatory requirements in Australia. By incorporating these standards into the platform, Microsoft Sustainability Manager ensures that organisations can easily produce reports that meet the specific demands of different stakeholders, whether they are regulators, investors, or customers.
Security and scalability are also key strengths of Microsoft Sustainability Manager. Built on the trusted Azure cloud platform, the solution offers robust data security features, ensuring data is protected against unauthorized access or breaches. Additionally, the platform’s cloud-based architecture allows it to scale according to the needs of the organisation, whether they are a small business just starting their sustainability journey or a large multinational corporation with complex data needs. This scalability ensures that the platform can grow with the organisation, adapting to new challenges and expanding regulatory requirements as they arise.
In addition to its technical capabilities, Microsoft Sustainability Manager integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products and services, such as Power BI, Dynamics 365, and Microsoft 365. This integration enhances the overall user experience by providing familiar tools and interfaces, making it easier for teams to collaborate and share insights across the organisation. It also allows for the integration of sustainability data with other business processes, such as financial reporting or supply chain management, providing a more comprehensive view of the organisation’s overall performance.
How Microsoft Sustainability Manager Helps with Reporting Obligations
- Centralized Data Management: One of the biggest challenges in sustainability reporting is the fragmented nature of data. Sustainability-related information often resides in silos, scattered across different departments, regions, and formats. Microsoft Sustainability Manager centralizes this data, bringing it together into a cohesive, manageable format. This ensures that all data points are accounted for and that there is a single source of truth for reporting purposes.
- Automated Reporting: The platform automates the generation of sustainability reports, reducing the time and effort required to compile data manually. This feature is particularly beneficial where timely and accurate reporting is critical. Automated reporting also reduces the risk of human error, ensuring that reports are reliable and meet the rigorous standards set by regulatory bodies.
- Compliance and Standards Alignment: Microsoft Sustainability Manager is designed to align with global and regional sustainability standards, including those required in Australia. The platform’s built-in templates and frameworks ensure that companies can easily adhere to specific reporting requirements, whether it’s for GHG emissions, energy consumption, or other critical sustainability metrics.
- Real-Time Insights and Forecasting: The platform offers real-time insights and predictive analytics, allowing organisations to not only understand their current sustainability performance but also to forecast future trends. This proactive approach enables companies to stay ahead of regulatory changes and make informed decisions that align with long-term sustainability goals.
- Customizable Dashboards and KPIs: Every organisation is unique, with different sustainability goals and reporting needs. Microsoft Sustainability Manager provides customizable dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs), enabling companies to tailor the platform to their specific requirements. This flexibility ensures that organisations can track and report on the metrics that matter most to them while still meeting external obligations.
Conclusion
As Australia continues to enforce stricter sustainability reporting requirements, organisations must adapt by enhancing their data management and reporting capabilities. Microsoft Sustainability Manager offers a comprehensive solution that not only simplifies the reporting process but also ensures that data is accurate, timely, and aligned with regulatory standards.
By placing data at the core of their sustainability strategy, organisations can not only meet their reporting obligations but also gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. Microsoft Sustainability Manager empowers companies to turn sustainability from a regulatory requirement into a strategic advantage, driving long-term success in a world where sustainability is increasingly paramount.